Bicipital Groove X Ray
This tool allows you to search snomed ct and is designed for educational use only.
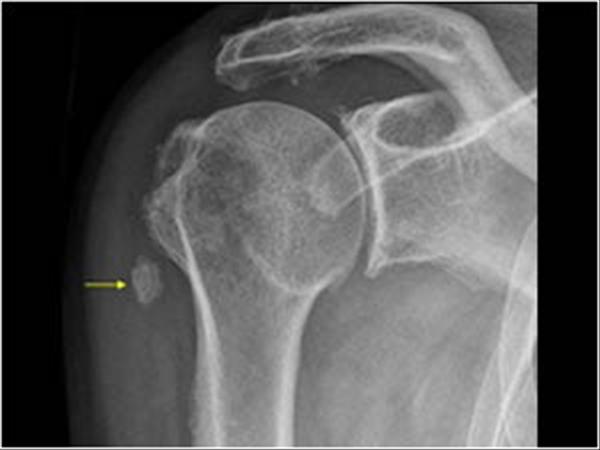
Bicipital groove x ray. Clinical information calcifications seen on x ray. Shoulder tangential intertubercular bicipital groove purpose and structures shown. Loose body and effusion in the biceps tendon sheath in a patient with omarthrosis x ray loose body and effusion in the biceps tendon sheath in a patient with omarthrosis details. Ultrasound images clips calcifications in the pectoralis major insertion that should not be mistaken for loose.
Coracoid process humeral head greater lesser tuberosity bicipital groove duration. O centered to the anterior part of the head of humerus. The effect of the direction of the x ray beam on the image of the groove was studied in cadaver specimens. Calcifications in the pectoralis major insertion that should not be mistaken for loose bodies in the biceps tendon sheath.
A standardized optimal x ray beam direction was subsequently used in a clinical study on 30 patients. The purpose of this paper was to find a standard radiographic view for measurements of the intertubercular groove of the human humeral head. Loose bodies in the bicipital groove pitfalls. In this project we investigate the relationship between the 3d shape of the bicipital groove and the incidence of pathology of the long biceps tendon.
We made special tangential views on 40 such patients and in no instance was a normal groove depicted. Pathologic changes in the bicipital groove region. The hand is rotated 45 degrees laterally from prone to bring the bicipital groove in profile centering o the of the beam central ray is directed cranially along the long axis of humerus. Bicipital groove x ray bicipital groove x ray procedure hide descriptions.
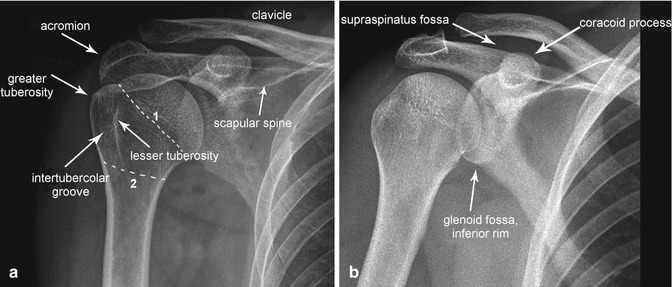
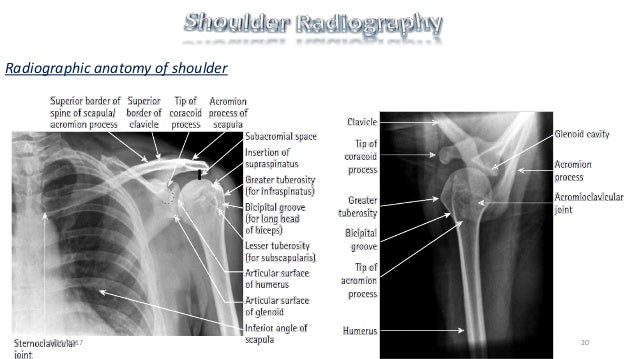
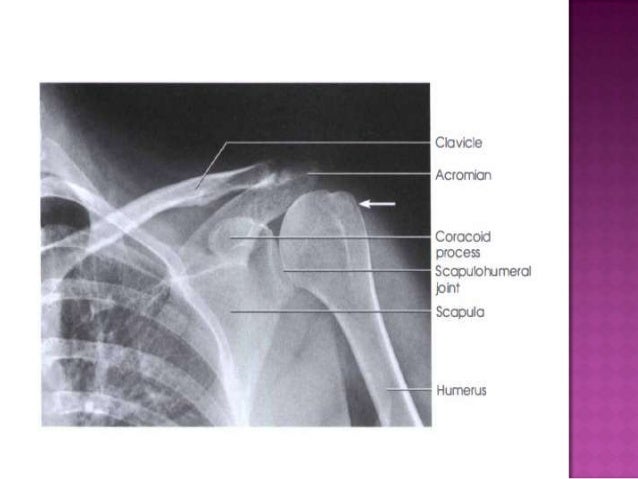
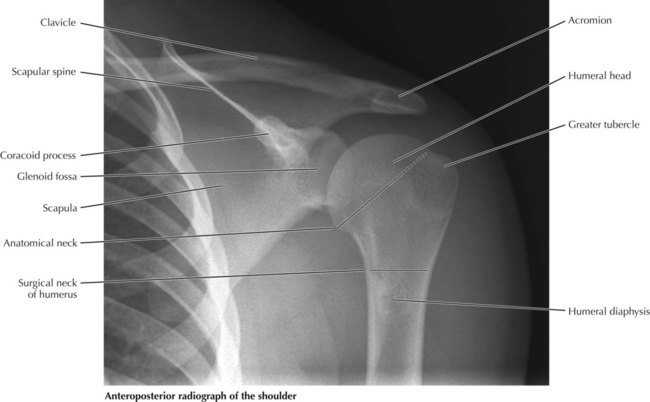
The bicipital groove is an osseous groove formed in the humeral head by the medial and lateral tuberosities. This view should demonstrate the bones and soft tissue of the shoulder specifically the intertubercular groove free of superimposition of the shoulder. Inflammation of the biceps tendon within the intertubercular bicipital groove is called primary biceps tendinitis which occurs in 5 percent of patients with biceps tendinitis 1 the 95 percent. It serves to retain the long head of the biceps brachii.
The noted anatomist.