Bicipital Groove Structures
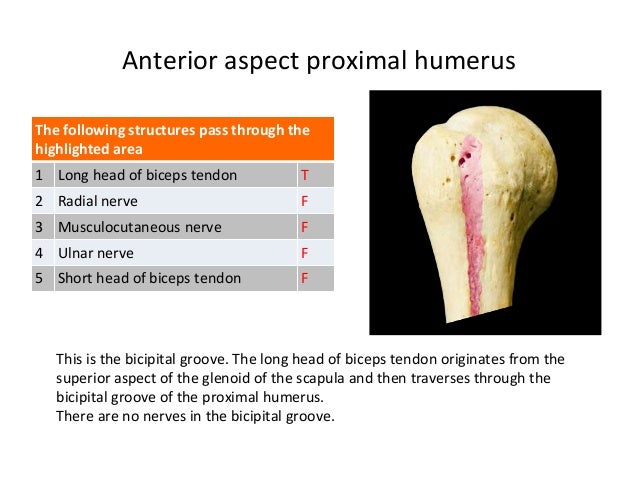
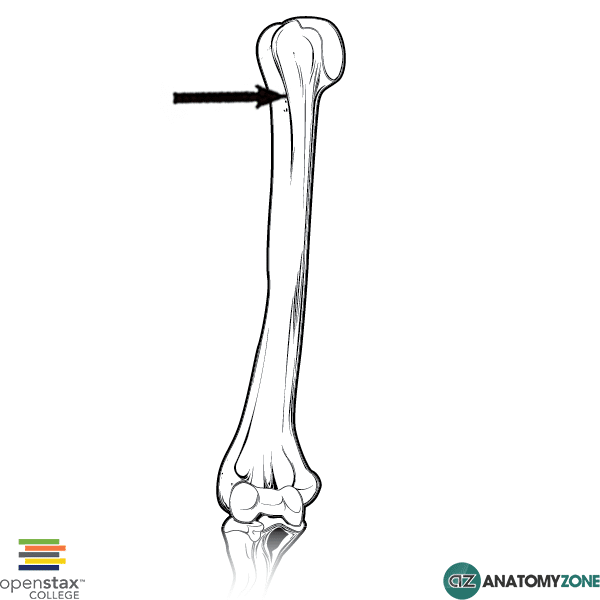
The structure indicated is the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus.
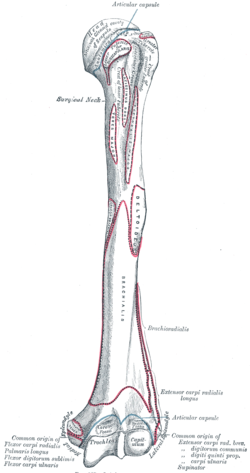
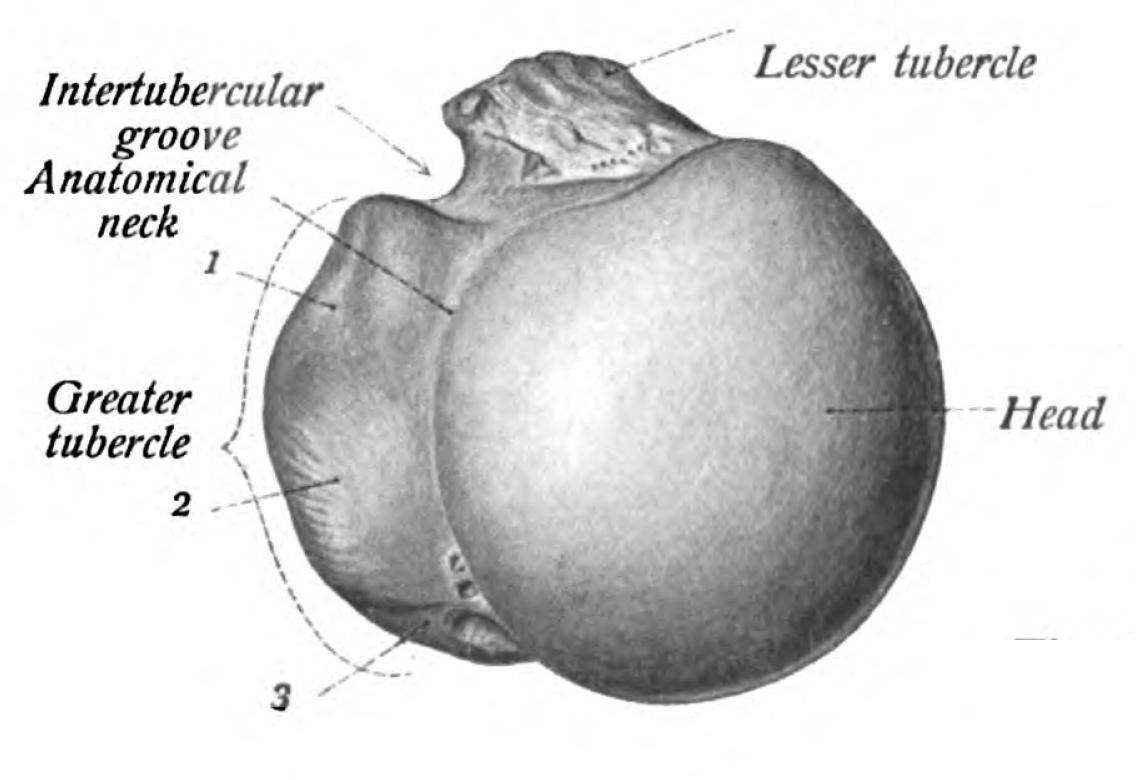
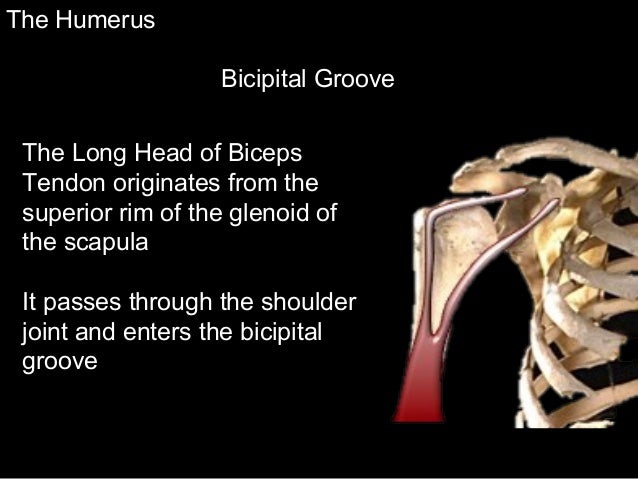
Bicipital groove structures. The bicipital groove is typically 4 6 mm deep 1. Upper extremity the upper extremity consists of a large rounded head joined to the body by a constricted portion called the neck and two eminences the greater and lesser tubercles. It should be distinguished from the bicipital groove or intertubercular sulcus which is not a surface anatomy structure. It is divisible into a body and two extremities.
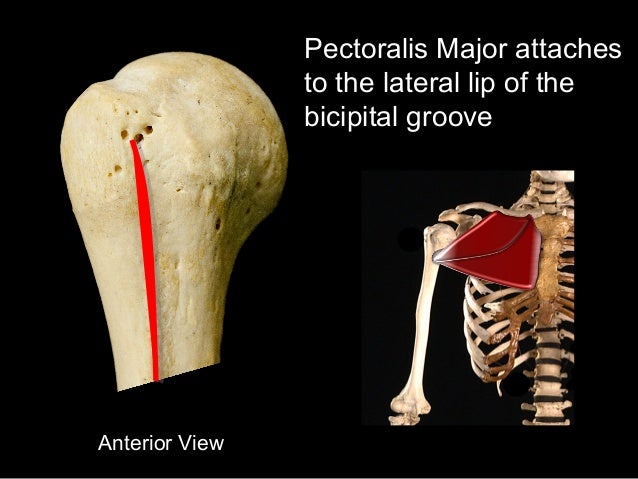
207 208 is the longest and largest bone of the upper extremity. The greater and lesser tubercles of humerus are separated from each other by a deep groove the intertubercular groove bicipital groove which lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii and transmits a branch of the anterior humeral circumflex artery to the shoulder joint it runs obliquely downward and ends near the junction of the upper with the middle third of the bone. The medial bicipital groove is seen on the surface anatomy of the upper arm it is formed by the longitudinal hollow between the biceps and triceps muscles. The bicipital groove is an anatomic landmark that sits between the greater and lesser tuberosities and its osseous and soft tissue components contribute to the inherent stability of the lhbt.
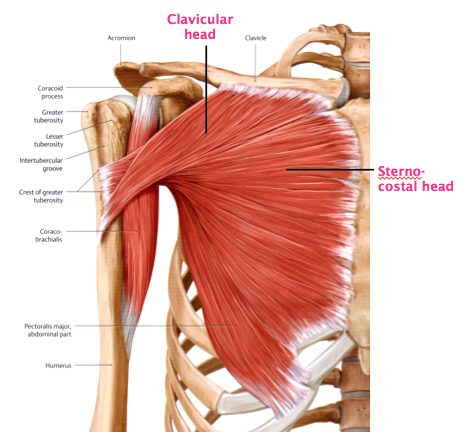
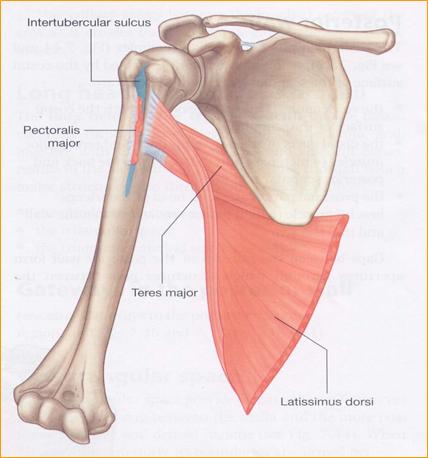
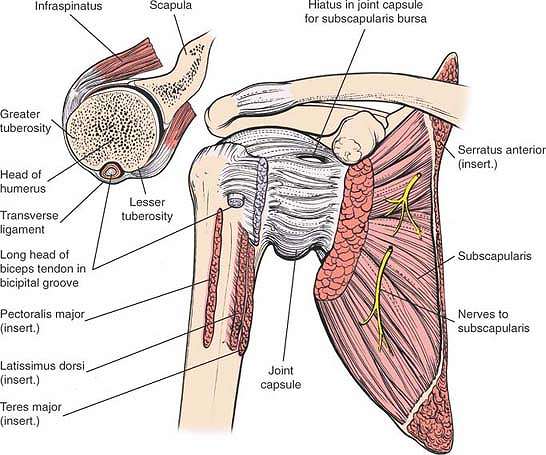
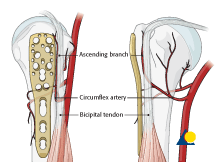
The intertubercular sulcus also known as the intertubercular groove or bicipital groove is a groove separating the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus. The bicipital groove intertubercular groove sulcus intertubercularis is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle the bicipital groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii between the tendon of the pectoralis major on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major on the medial lip. It may also cause thrombosis of the ascending branch of the anterior circumflex humeral artery running in the bicipital groove creating ischaemia in the structures supplied by this artery. It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral.
L bis twice caput head. The pulse of the brachial artery can be felt in the medial bicipital groove. The tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle runs in this groove and attaches on the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. It contains the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle which is ensheathed in a synovial reflection of the.
Bicipital groove is often used as an important landmark for proper orientation of humeral prosthesis especially in the case of a fracture. D groeve a groove between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus for passage of the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle. The head caput humeri the head nearly hemispherical in form 54 is. The bicipital groove also known as the intertubercular sulcus or sulcus intertubercularis is the indentation between the greater and lesser tuberosities of the humerus that lodges the biceps tendon.