Bicipital Groove Radiopaedia
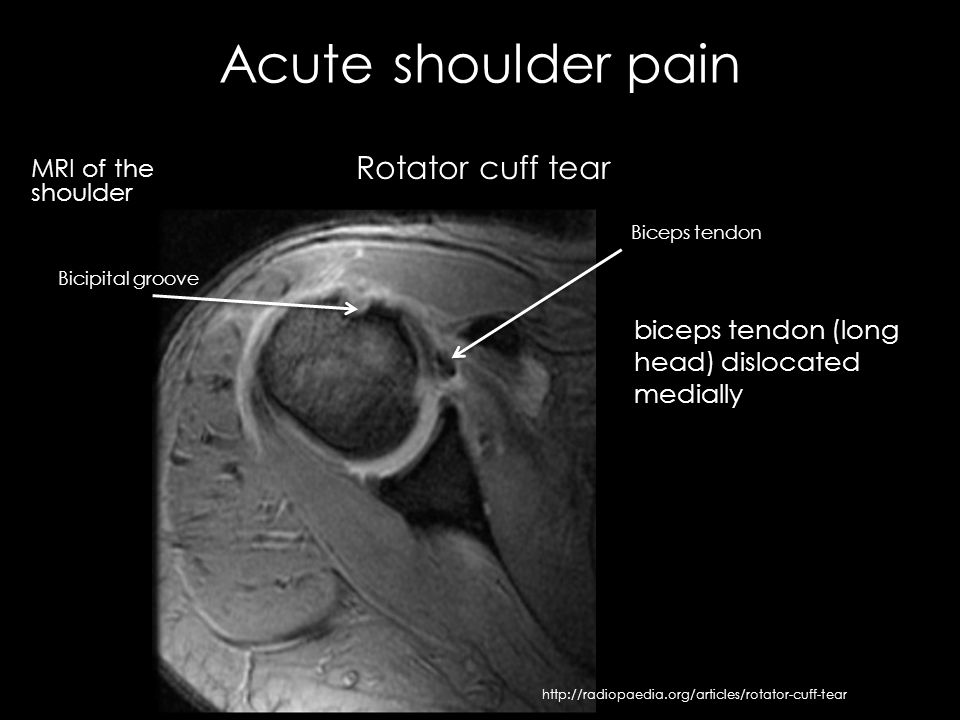
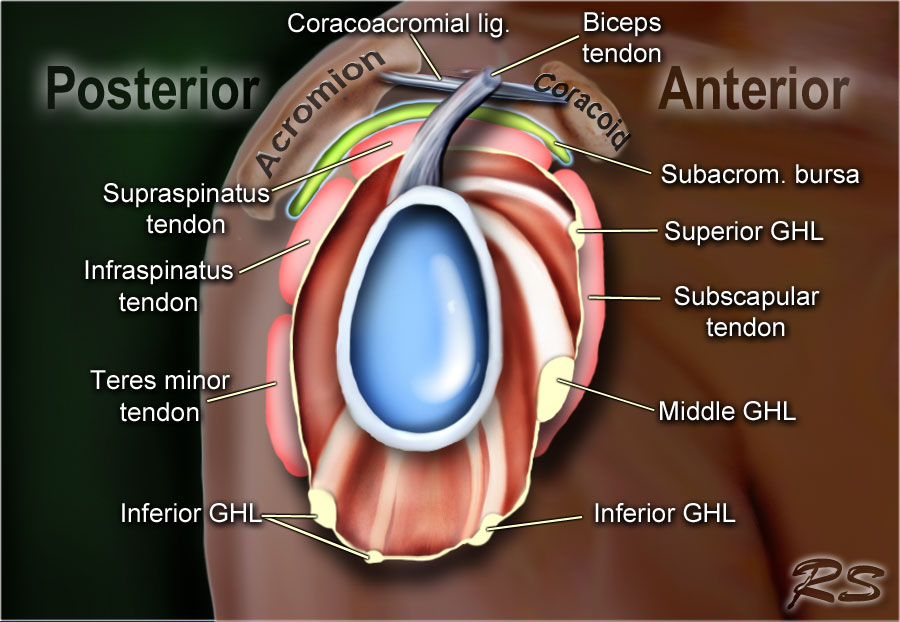
The bicipital groove also known as the intertubercular sulcus or sulcus intertubercularis is the indentation between the greater and lesser tuberosities of the humerus that lodges the biceps tendon.
Bicipital groove radiopaedia. In more specialized departments full length spine radiography via projectional ct or slit beam digital radiography is still frequently utilized in the diagnosis and management of scoliosis. This article aims to frame a general concept of an mri protocol for the assessment of the pelvis in the setting of suspected musculoskeletal p. Radiopaedia is a rapidly growing open edit educational radiology resource which has been primarily compiled by radiologists and radiology trainees from across the world. The long head of biceps lhb tendon is usually located inferiorly in the bicipital groove held there by the biceps pulley the stabilization role of the transverse humeral ligament is controversial 3 as it moves superiorly it arches through the rotator cuff interval where it is held by a sling.
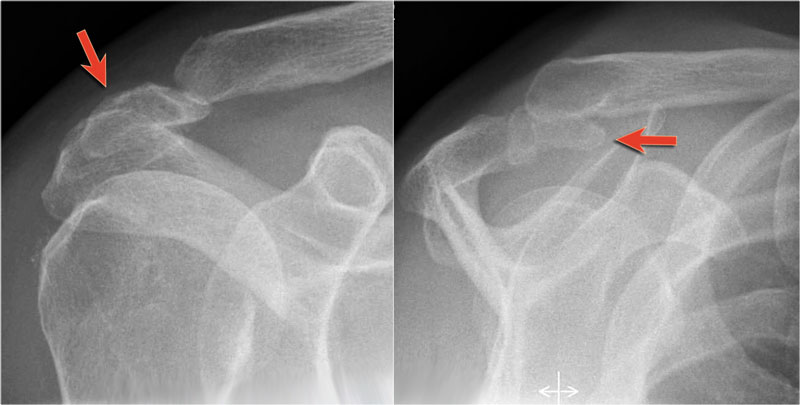
Check for errors and try again. The tendon of the subscapularis muscle attaches both to the lesser tubercle aswell as to the greater tubercle giving support to the long head of the biceps in the bicipital groove. Dislocation of the long head of the biceps will inevitably result in rupture of part of the subscapularis tendon. Spine radiography is utilized in both trauma and general imaging.
Spine radiography explores the cervical thoracic lumbar and sacral regions. Our mission is to create the best radiology reference and to make it available for free forever. It contains the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle which is ensheathed in a synovial reflection of the. The bicipital groove is typically 4 6 mm deep 1.
Long head of biceps can be affected by numerous pathological processes 3. A thickened and edematous lbt arrows is identified anterior to the humerus at a level distal to the bicipital groove outlined by surrounding mild edema. The mri pelvis protocol encompasses a set of mri sequences for the routine assessment of pelvis. High t2 signal intensity noted at the of this humeral head at the biceps groove.
Dislocation of the long head of biceps tendon is one of the complications of shoulder injury. An irregular tear of the superior glenoid labrum is also demonstrated short arrow. High t2 fluid signal intensity is noted around the thickened biceps tendon which is seen within its groove suggestive of tenosynovitis. Unable to process the form.
Thickened with intermediate high t2 signal intensity noted at the supraspinatus tendon suggestive of tendinosis.