Bicipital Groove Fluid

More cranially the biceps tendon is held in the bicipital groove by the transverse humeral ligament believed to be an extension of the subscapularis tendon that covers the bicipital groove.
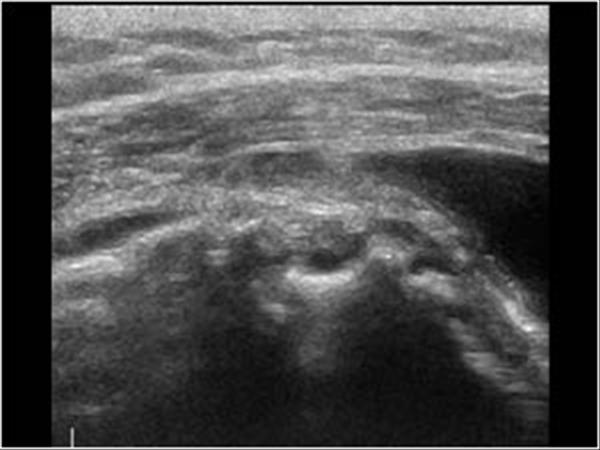
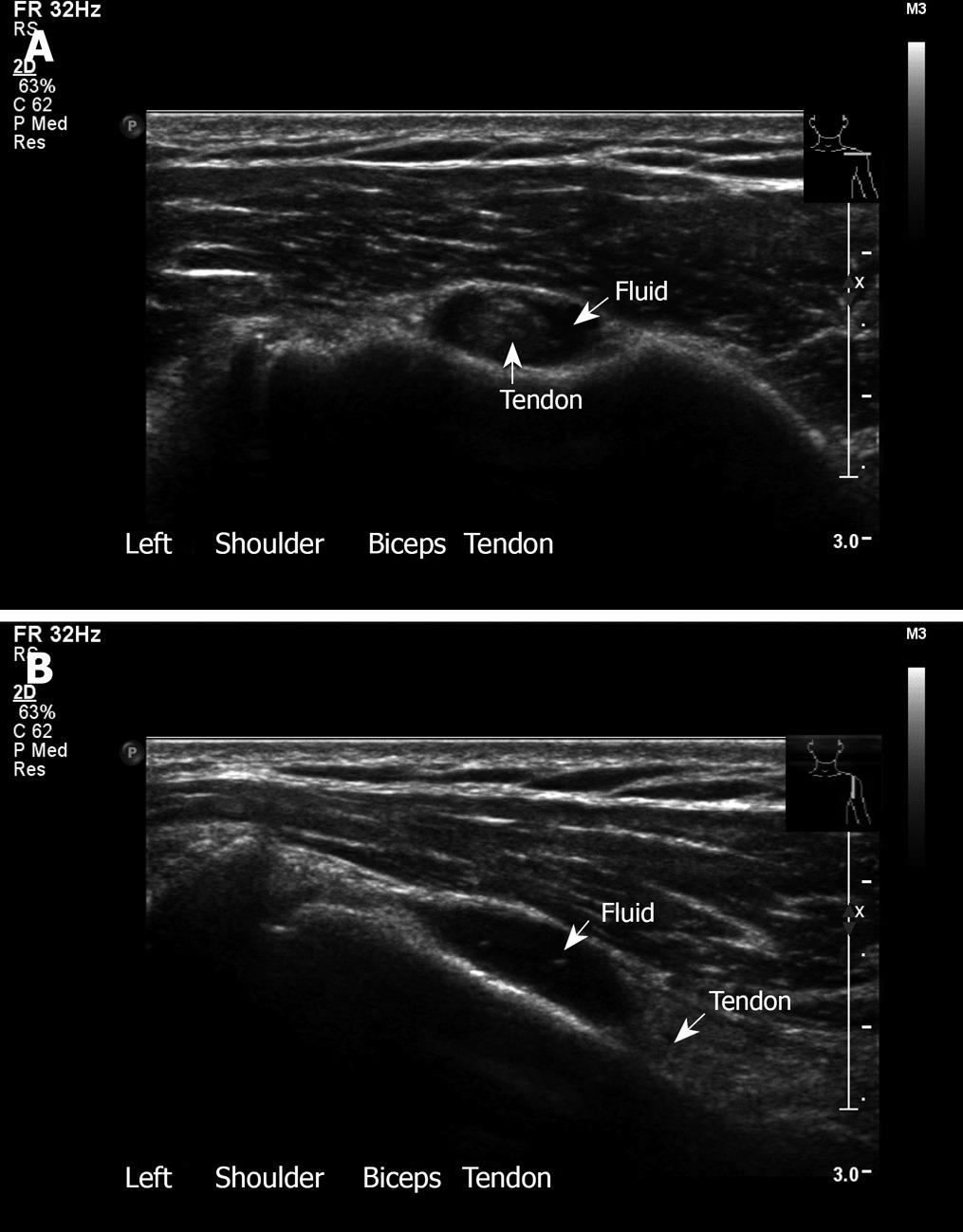
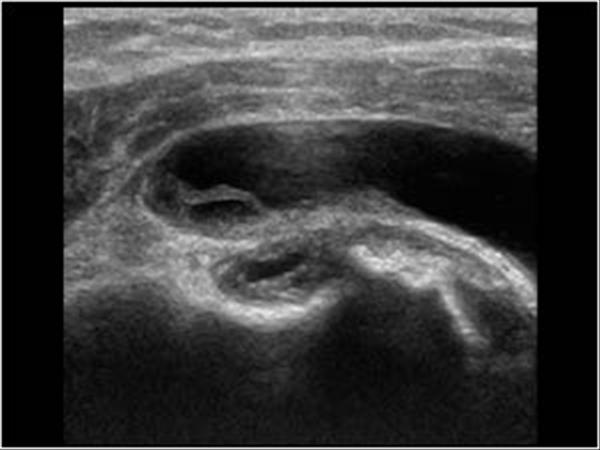
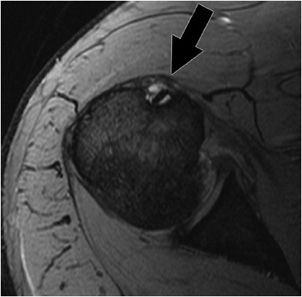
Bicipital groove fluid. Bicipital peritendinous effusion bpe is the most common biceps tendon abnormality and can be related to various shoulder ultrasonographic findings. Thickened with intermediate high t2 signal intensity noted at the supraspinatus tendon suggestive of tendinosis. The needle should enter the skin at 30 and be directed parallel to the groove. Long head of biceps can be affected by numerous pathological processes 3.
Inflammation of the biceps tendon within the intertubercular bicipital groove is called primary biceps. Since the association of bpe with subacromial. Bicipital tenosynovitis is a pathological condition in which there is inflammation of the tendon sheaths that surround the biceps tendons. High t2 signal intensity noted at the of this humeral head at the biceps groove.
X rays may reveal mineralization of the biceps tendon mineralization within the biceps groove or sclerosis hardening of the bone seen as increased whiteness on x rays below the biceps groove. Fluid in the biceps tendon sheath can indicate tenosynovitis but also may be a normal finding when fluid is present in the glenohumeral joint because the biceps tendon sheath communicates with the joint. Long head of biceps brachii tendon pathology can be examined both with ultrasound and or mri. High t2 fluid signal intensity is noted around the thickened biceps tendon which is seen within its groove suggestive of tenosynovitis.
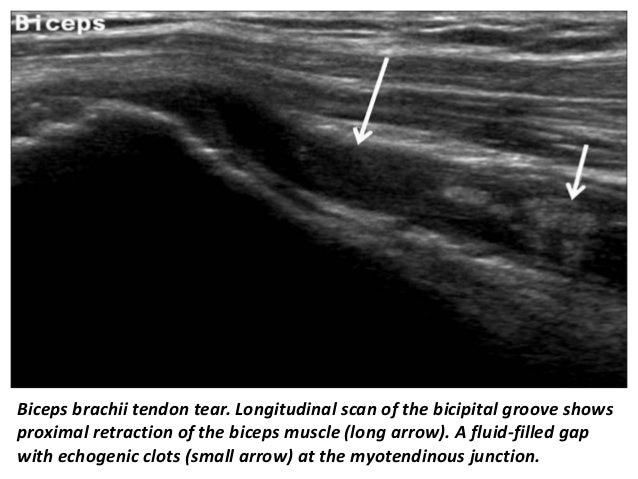
Bicipital tenosynovitis can be a result of many small tears resulting in inflammation over a period of a number of years or due to an acute injury to the biceps region. To inject into the area of the long head of the biceps tendon the needle is inserted directly into the most tender area over the bicipital groove. The tendon is exposed on the anterior shoulder as it passes through the humeral bicipital groove and inserts onto the superior aspect of the labrum of the glenohu. With the patient sitting or lying the biceps tendon is identified in the groove and the point of insertion noted.
Tenosynovitis of the lhbt can be seen as an isolated finding or more commonly in patients with an impingement syndrome or rotator cuff tear. Both instability and tears can result in pain and decreased function. Biceps tendinitis is a disorder of the tendon around the long head of the biceps muscle.