Bicipital Groove Fluid Mri

Shoulder anatomy mri normal anatomy variants and checklist.
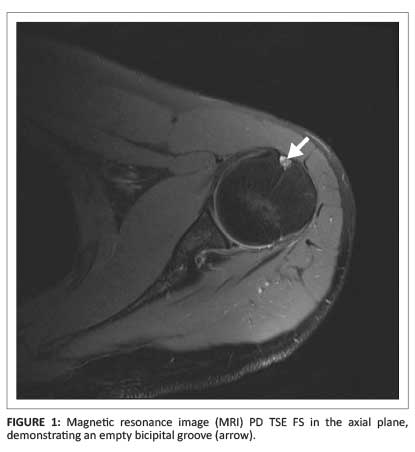
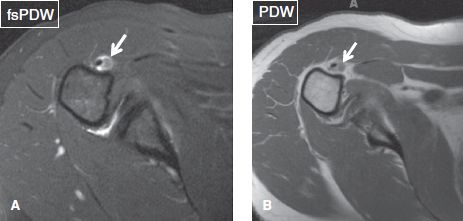
Bicipital groove fluid mri. The fibers of the subscapularis tendon hold the biceps tendon within its groove. Bicipital tenosynovitis can be a result of many small tears resulting in inflammation over a period of a number of years or due to an acute injury to the biceps region. Bicipital tenosynovitis is a pathological condition in which there is inflammation of the tendon sheaths that surround the biceps tendons. In that situation no intraarticular fluid or contrast extension into the intertubercular groove is seen at mri view larger version 249k fig.
Inflammation of the biceps tendon within the intertubercular bicipital groove is called primary biceps. A thickened and edematous lbt arrows is identified anterior to the humerus at a level distal to the bicipital groove outlined by surrounding mild edema. An irregular tear of the superior glenoid labrum is also demonstrated short arrow. Nodular soft tissue debris and small calcifications may be seen within the fluid.
Both instability and tears can result in pain and decreased function. There may be evidence of distention of the bicipitoradial bursa by fluid which appears anechoic or hypoechoic soft tissue. Ular fluid or contrast extension into the inter tubercular groove is seen at mri 2 fluid in the biceps tendon sheath can in dicate tenosynovitis but also may be a nor mal finding when fluid is present in the gle nohumeral joint because the biceps tendon sheath communicates with the joint. Power doppler imaging may show hyperemia and suggests active inflammation.
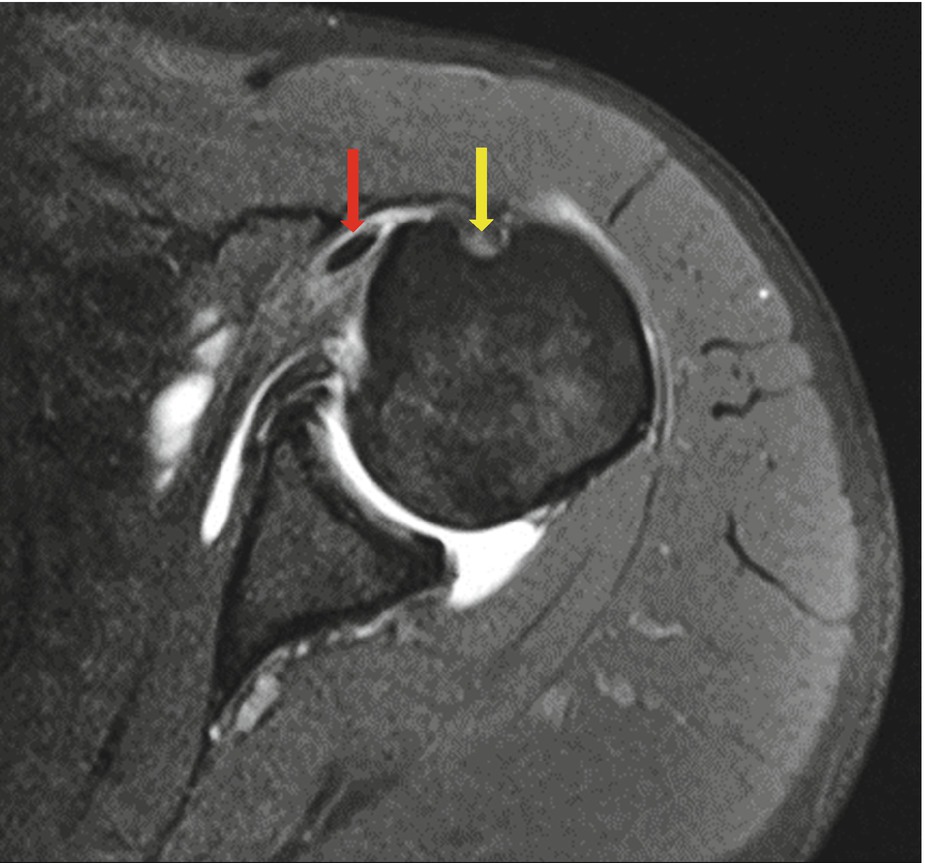
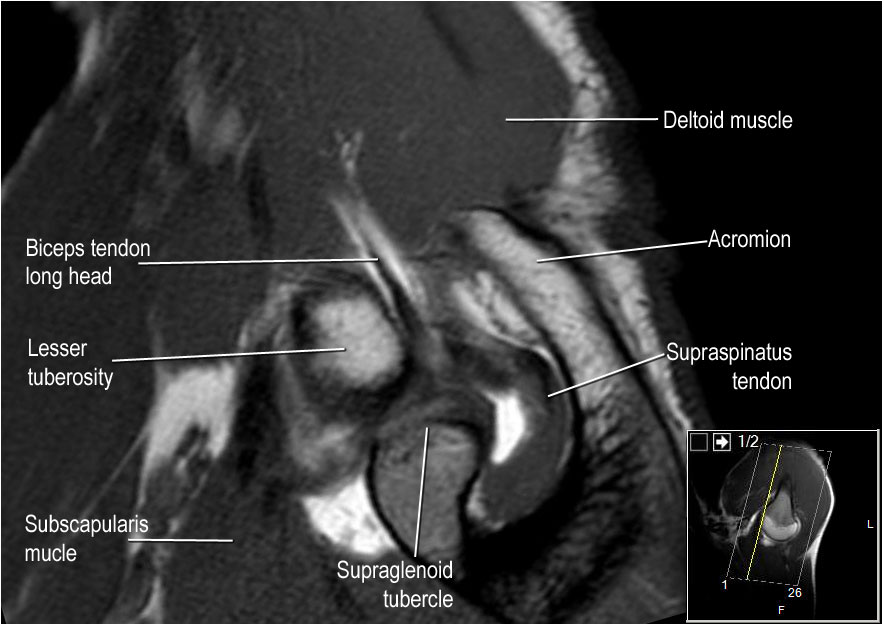
The bicipital groove is typically 4 6 mm deep 1. Look for excessive fluid in the subacromial bursa and for tears of the supraspinatus tendon. Thickened with intermediate high t2 signal intensity noted at the supraspinatus tendon suggestive of tendinosis. It contains the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle which is ensheathed in a synovial reflection of the.
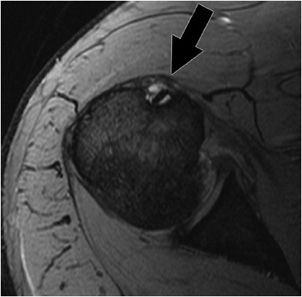
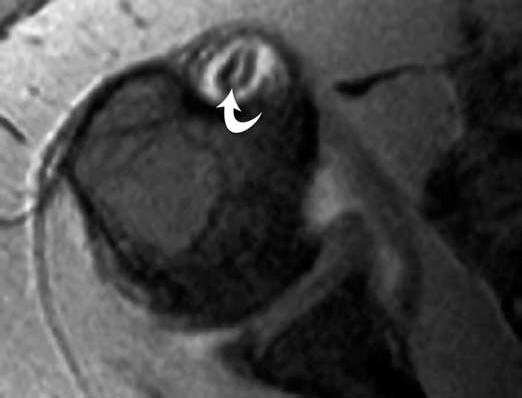
The bicipital groove is empty with no biceps tendon arrowhead. High t2 signal intensity noted at the of this humeral head at the biceps groove. The bicipital groove also known as the intertubercular sulcus or sulcus intertubercularis is the indentation between the greater and lesser tuberosities of the humerus that lodges the biceps tendon. Long head of biceps brachii tendon pathology can be examined both with ultrasound and or mri.
High t2 fluid signal intensity is noted around the thickened biceps tendon which is seen within its groove suggestive of tenosynovitis. Biceps tendinitis is a disorder of the tendon around the long head of the biceps muscle. Teno synovitis of the lhbt can be seen as an.