Bicipital Groove Bone
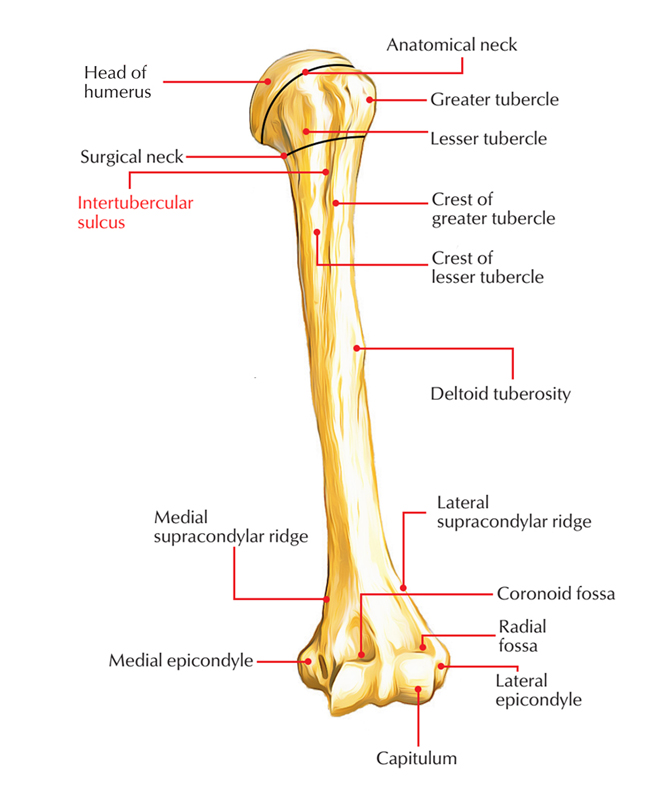
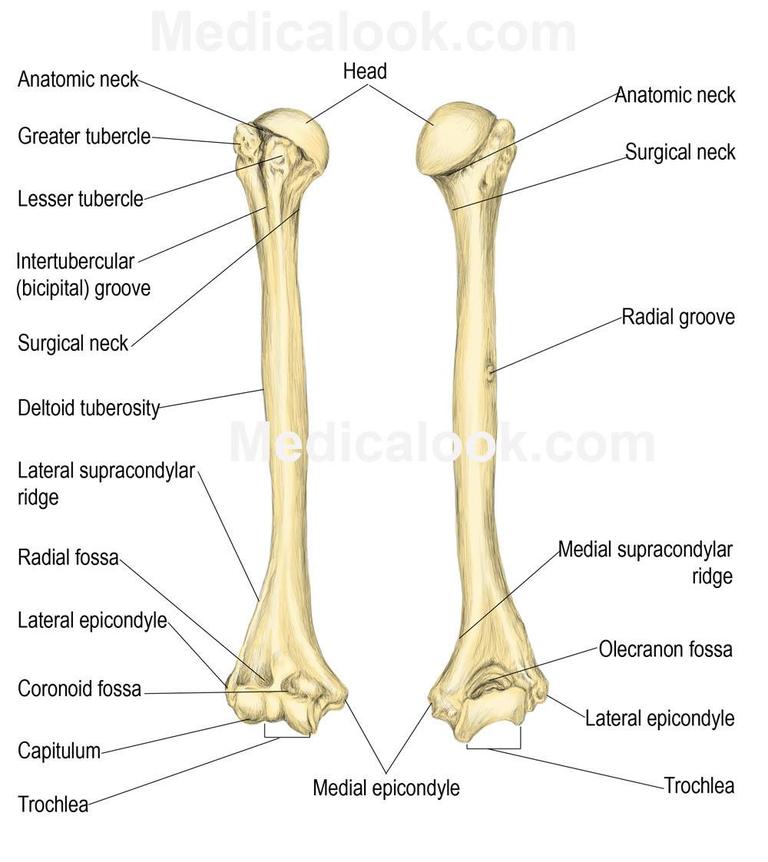
Bicipital groove of right humerus.
Bicipital groove bone. The biceps tendon originates from the front part of the scapula shoulder blade. Bicipital tenosynovitis is inflammation of the origin of the biceps tendon and its surrounding tendon sheath. The tendon crosses the shoulder joint passes through the bicipital groove of the humerus and widens into the biceps muscle which attaches onto the radius. The biceps is a muscle located at the front of your upper arm and it helps the elbow flex bend.
The medial lip the floor and the lateral lip. It runs obliquely downward and ends near the junction of the upper with the middle third of the bone. The lesser tuberosity is directed anteriorly. The most common treatment for bicipital tenosynovitis is conservative treatment with physical therapy and exercises.
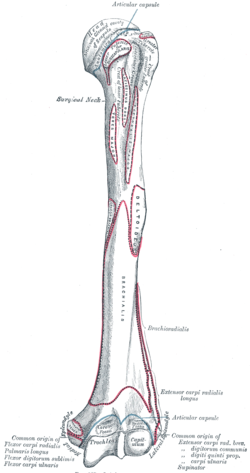
The shoulder is a ball and socket joint. The insertion of the latissimus dorsi is found along the floor of the bicipital groove. The groove is occupied by a long head of biceps tendon surrounded by synovial sheath and ascending branch of the anterior circumflex humeral artery. Tendons attach muscle to bone.
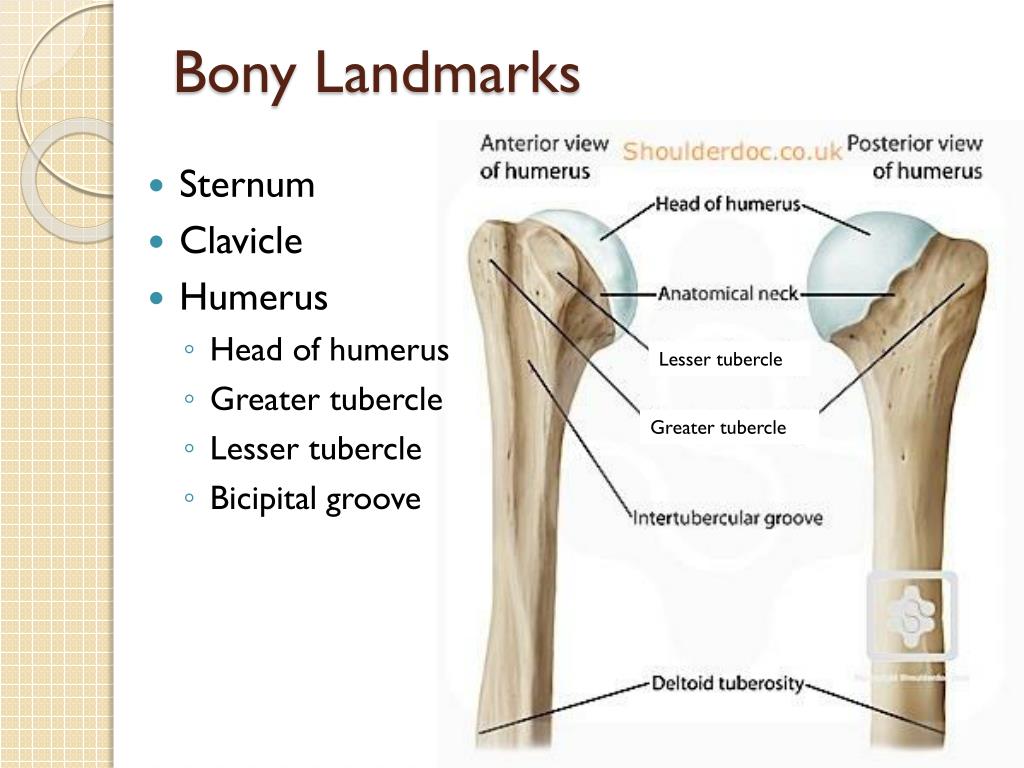
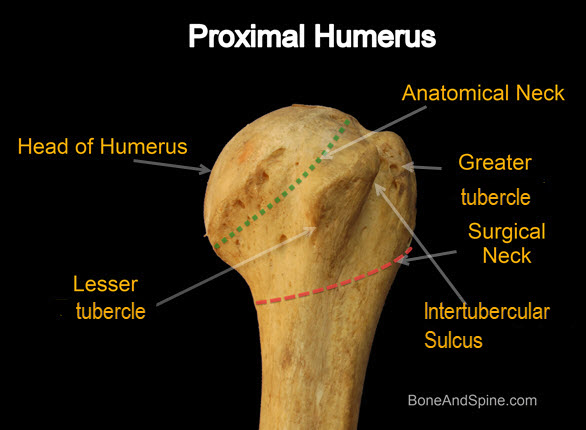
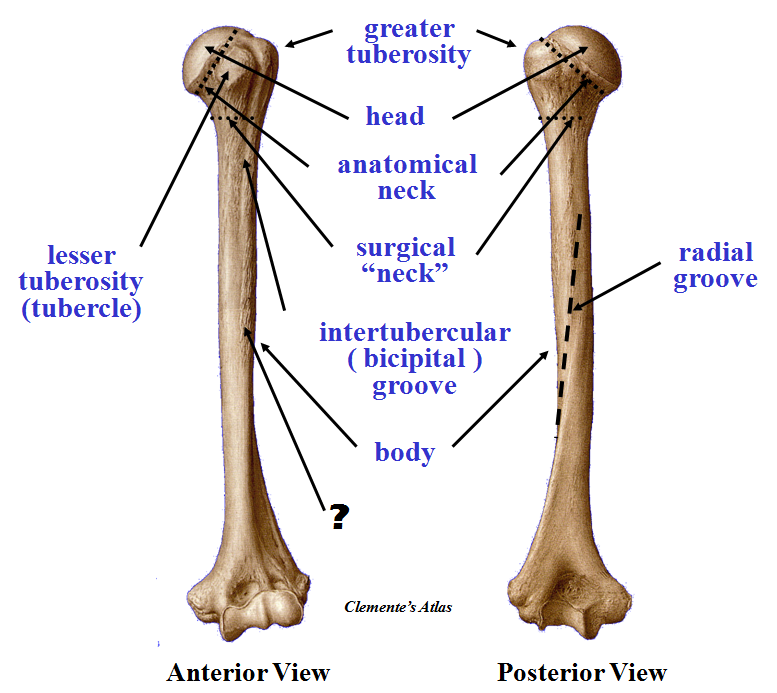
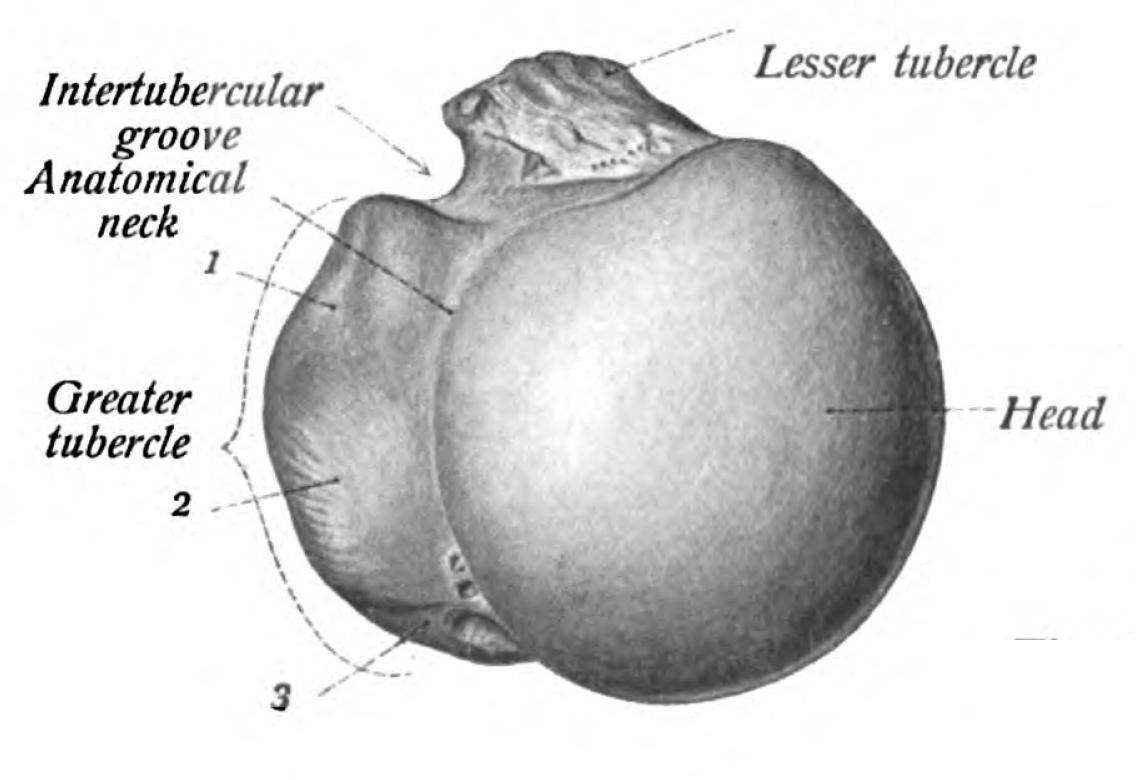
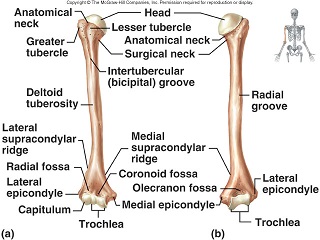
The tubercles are separated from each other by a deep groove the intertubercular groove bicipital groove which lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii and transmits a branch of the anterior humeral circumflex artery to the shoulder joint. The bicipital groove bg of the proximal humerus is a groove in the humeral head formed by the medial and lateral tuberosities fig. The bg prevents the lbt from dislocating during movement of the arm. The greater tuberosity is directed laterally.
The teres major inserts on the medial lip of the groove. The transverse humeral ligament connects the lesser and greater tubercles. It is the lateral wall of the axilla. The long head of biceps brachii muscle runs along this groove.
It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral. The intertubercular groove or also known as the bicipital sulcus is a deep groove that begins between the two tubercles and extends longitudinally down the proximal shaft of the humerus. A bony bridge has been observed over the bicipital groove in a humerus. When examining the biceps region radiologically in cases of bicipital tenosynovitis there will be significant calcification of the tendon and presence of bone spurs in the intertubercular groove.
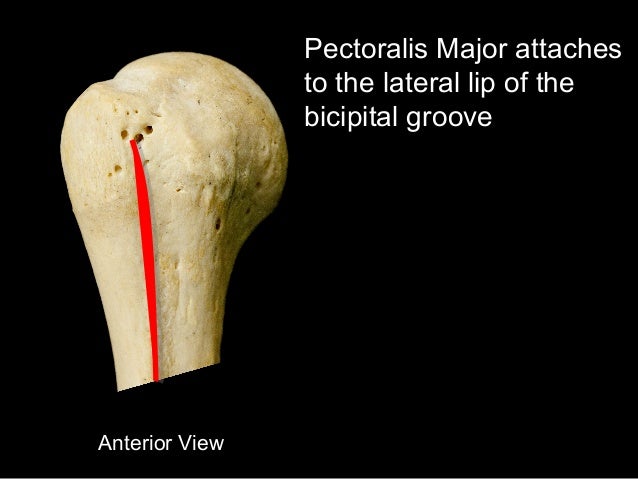
The complete ossification of the transverse humeral ligament or muscle fibres is being reported for the first time. The bicipital groove intertubercular groove sulcus intertubercularis is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle the bicipital groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii between the tendon of the pectoralis major on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major on the medial lip. It runs obliquely downward and ends near the junction of the upper with the middle third of the bone.