Bicipital Groove Anatomy

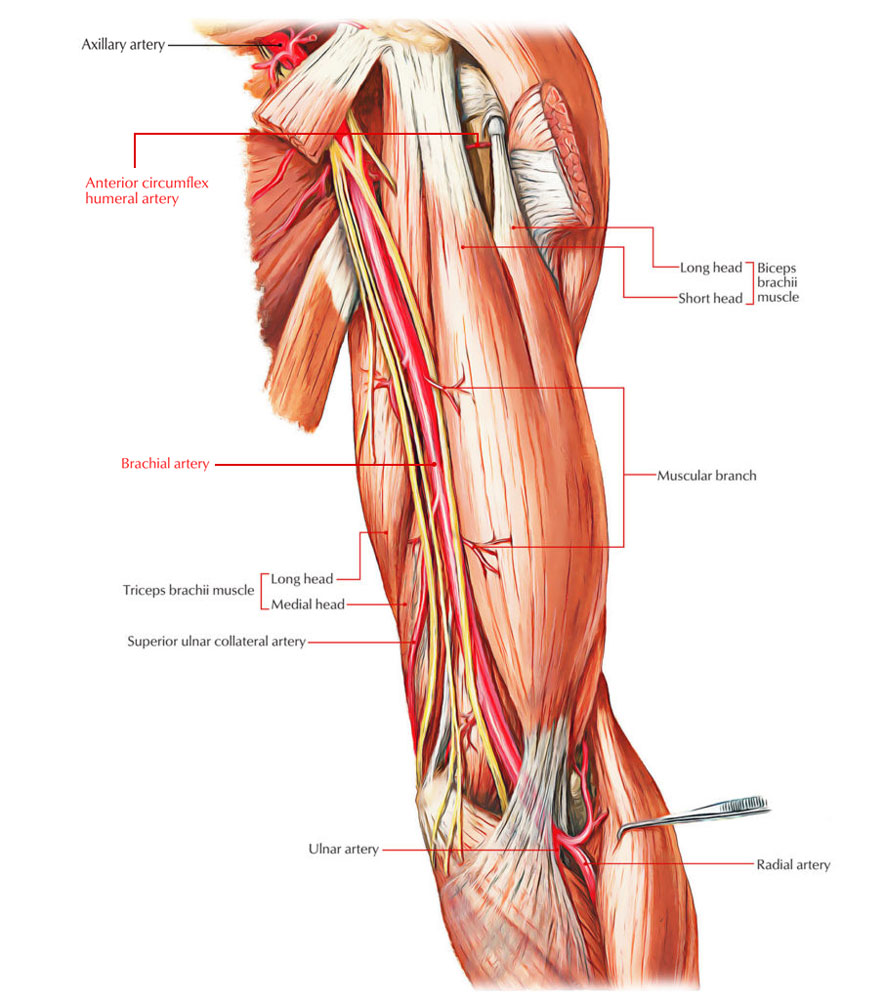
The pulse of the brachial artery can be felt in the medial bicipital groove.
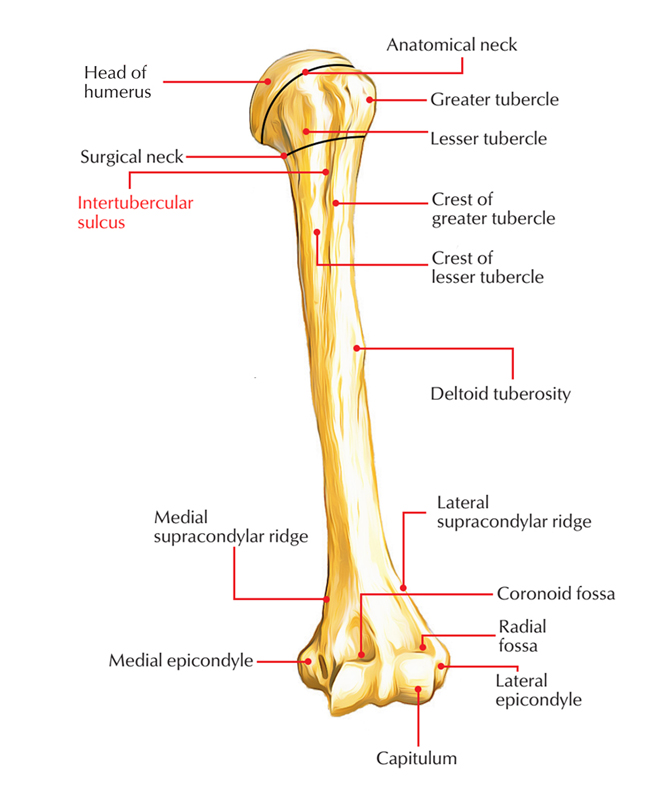
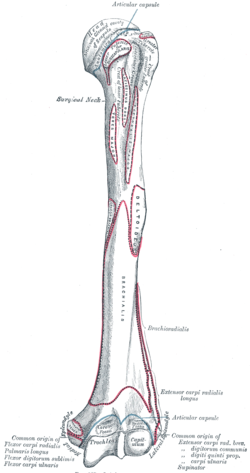
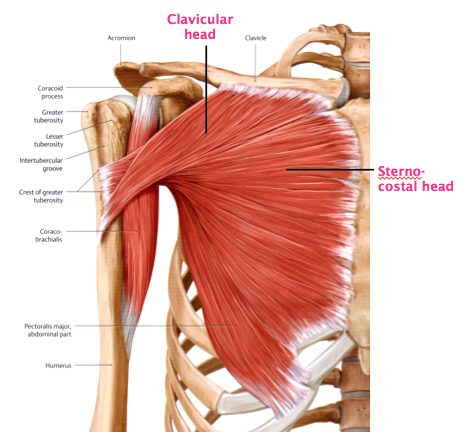
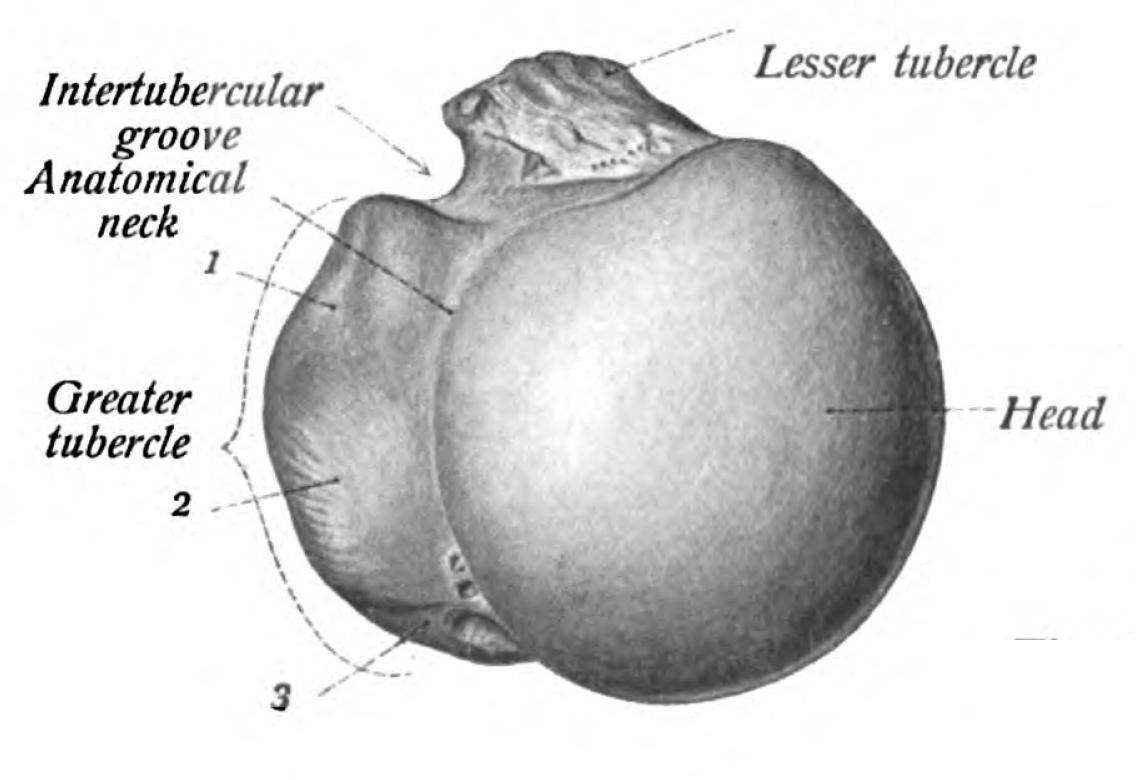
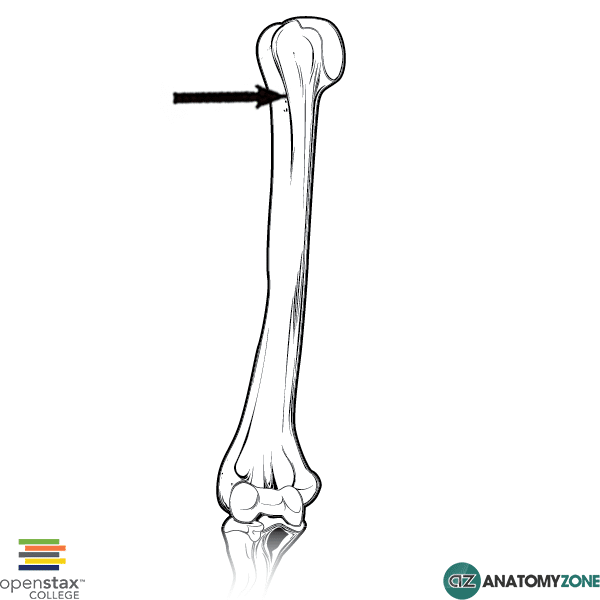
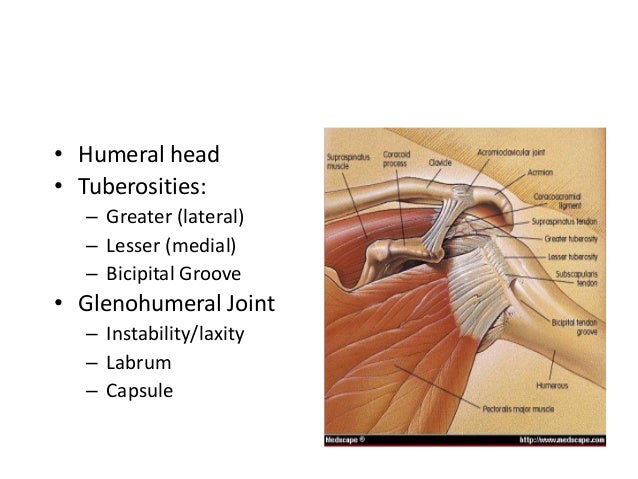
Bicipital groove anatomy. The medial bicipital groove is seen on the surface anatomy of the upper arm it is formed by the longitudinal hollow between the biceps and triceps muscles. The bicipital groove is typically 4 6 mm deep 1. Abstract introduction pathology in the bicipital groove can be a source of anterior shoulder pain. The bicipital groove intertubercular groove sulcus intertubercularis is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle the bicipital groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii between the tendon of the pectoralis major on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major on the medial lip.
It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral. Many studies have compared treatment techniques for the long head biceps tendon lhbt without sho. It contains the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle which is ensheathed in a synovial reflection of the. The greater and lesser tubercles of humerus are separated from each other by a deep groove the intertubercular groove bicipital groove which lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii and transmits a branch of the anterior humeral circumflex artery to the shoulder joint it runs obliquely downward and ends near the junction of the upper with the middle third of the bone.
The bicipital groove intertubercular groove sulcus intertubercularis is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle the bicipital groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii between the tendon of the pectoralis major on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major on the medial lip.